The comparison of home prices to buyers’ incomes is a popular measure for assessing the health of the real estate market. Presently, that multiple seems high, and people are using it to cry, crisis! But is this true?
Amy Nixon posts on Twitter (now known as X):
All of economics is supply and demand.
The median household to median income argument makes sense only in an economy where we have built enough housing units per capita, and every housing unit is being allocated as a family shelter unit because it serves no other economic utility
The model breaks down when you have wealthy families buying 3-4 spare vacation homes. And mom and pop landlords hanging onto starter homes when they upsize. And institutions buying millions of single family homes. And single people living alone in two units instead of coupling to buy one unit. And foreign citizens buying homes. And people buying and using 2 million single family homes as hotels (Airbnbs)
So long as single family residential housing is viewed as and can be used as an investment or luxury item beyond owner-occupied shelter and we don’t build enough homes to offset all those other uses, the ratio pictured in the infographic below can (and will) go even higher over time
It’s not 1985. And it’s never going to be 1985 again.
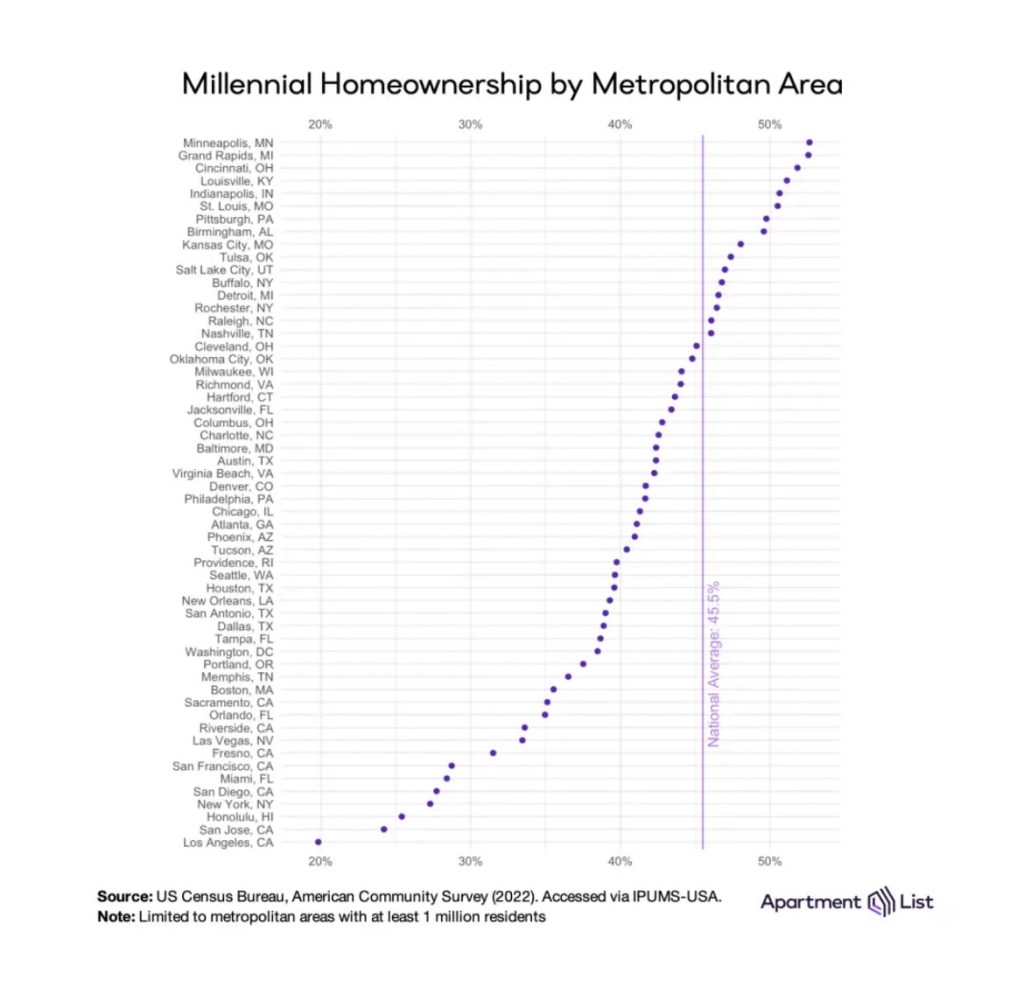
What Amy says is that there is a mix of home-ownership types. If you are analyzing Lake Country, with many second homes, there will be a different price-to-income figure than if you consider a first-tier suburb built almost exclusively of starter homes. I like to call them platters. It’s the local eco-systems of properties that have interesting numbers. Averaging just smudges out all the details.
I’ll also note the shift in demographic mix. The number of first-time buyers is at an all-time low. From NAR:
WASHINGTON (November 4, 2025) – The share of first-time home buyers dropped to a record low of 21%, while the typical age of first-time buyers climbed to an all-time high of 40 years, according to the National Association of REALTORS®’ 2025 Profile of Home Buyers and Sellers. This annual survey of recent home buyers and sellers covers transactions between July 2024 and June 2025 and offers industry professionals, consumers, and policymakers detailed insights into homebuying and selling behavior.

Repeat buyers enter the market with equity. They do not need to take on as much debt relative to their income as first-time buyers do. Yet the sales price is the measure from which payment is extrapolated, not the actual payment. As a market rises, so does the equity, pushing this fictitious measure of debt load out of whack with reality.