In days of yore, there was the market and the state. Two separate spheres of activity coexisted. And when private industry did not come through for the people, in the way they thought it should, market failure was the name given to assign blame. When the market failed, it was up to the state to address the lack of supply in areas such as medical care, poverty alleviation, housing, and the like.
One of economist Tyler Cowen’s first books addresses this trigger for state action in a compilation of thoughts on The Theory of Market Failure: A Critical Examination. But he isn’t convinced. He seems to say that when you look so closely at a tiny segment of a large system, you don’t see anything at all.
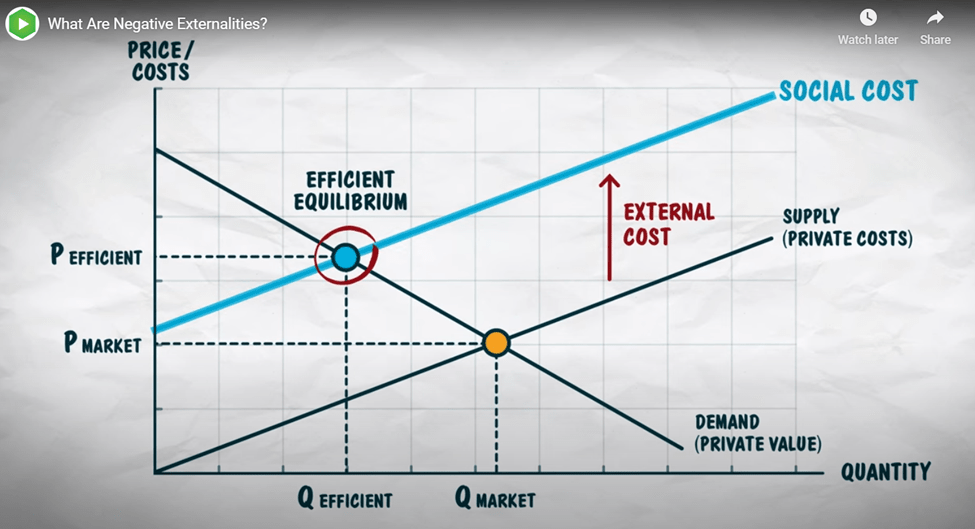
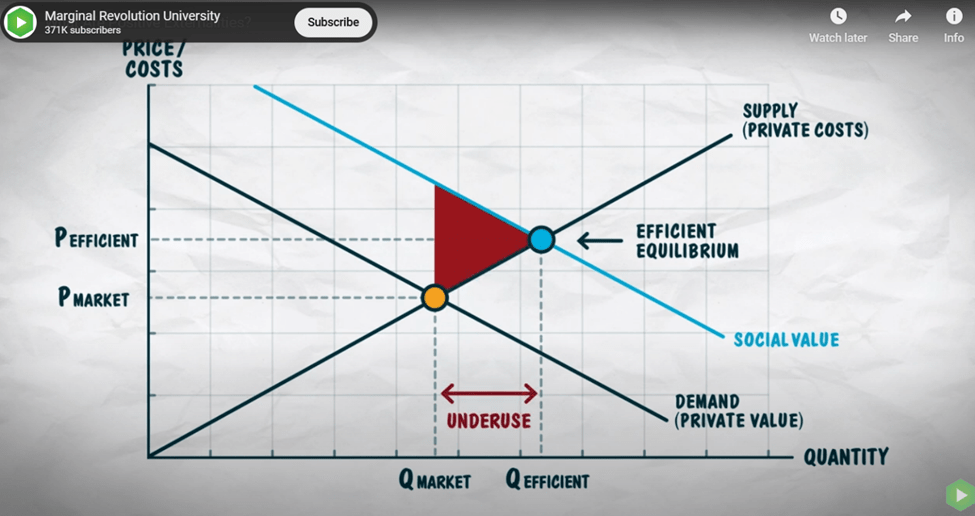
Consider externalities, a key signal that the market is merely pushing a problem onto some unsuspecting observer. He claims that (nearly) every single transaction has a positive or negative external effect. And, if you think about it, it’s true. We are social creatures. Although many consumptions are deeply personal, in the end, we always touch the lives of others.
The scope of the externalities/nonexcludability issue is vast. Nearly every concern of economic policy, from environmental considerations to research and development, involves externality problems. No one would claim that every instance of an externality warrants state intervention. There is no doubt, however, that the existence of externalities is one of the most powerful arguments for public sector involvement in the provision of public goods.
This isn’t the proper trigger for government intervention.
What about when the price seems too high, as in housing, or too low, as in wages? Whether a good is mediated through the private or public sector, prices still carry the most valuable form of comparative value information.
As noted earlier, the theory of public goods and externalities implies that if a good is characterized by nonrivalrous consumption, allowing additional individuals to consume it entails zero marginal cost. Demsetz’s arguments (1964; 1970) imply that this is only true in the presence of perfect information. Otherwise, allowing additional individuals to consume a good free of charge results in the abandonment of the price system in that sphere of activity. Since the publication of Hayek 1945, the role of prices in communicating information has been well known. In the provision of public goods as well as private goods, sacrificing such information may entail significant costs.
Prices are the most critical form of encapsulation of what groups of exchangers say about an exchange. We may not always conduct a thorough analysis of prices. That might be where the problem lies.
For instance, the exchange might be telling something vital about a group of people that others are simply not attuned to. People join various clubs throughout their lives. And these associations create structures of value.
The next two selections in section 2 of this volume discuss the nature of local public goods. Because such goods, by definition, can be provided to only a segment of a nation or community, determining which individuals will receive them becomes part of the economic problem. Once club or community membership becomes endogenous, many of Samuelson’s conclusions do not hold.
When people leave or join a club, when they exit or stay loyal, they impact how much of a surcharge the group of people in the club can charge.
The Tiebout model avoids the preference revelation problem; an individual’s preferences are revealed by his choice of location. It also avoids the free-rider problem; those who choose to belong to a given community are subject to the taxes or user fées that finance the provision of goods. Nor is pricing inefficiency a problem. If an individual is inefficiently excluded from the use of a public good or service, he can simply move to a community where that exclusion is not practiced.
The introduction written by Tyler Cowen is comprehensive. To the engaged observer, he dispels the dichotomy between industry and the state. There’s something pluristic out there. It’s big, messy, and complicated. It dovetails into many of the things people talk about under the titular of institutions. But it has structure– once you stand back and take a look.
That’s the project of the moment: a unified theory of price.