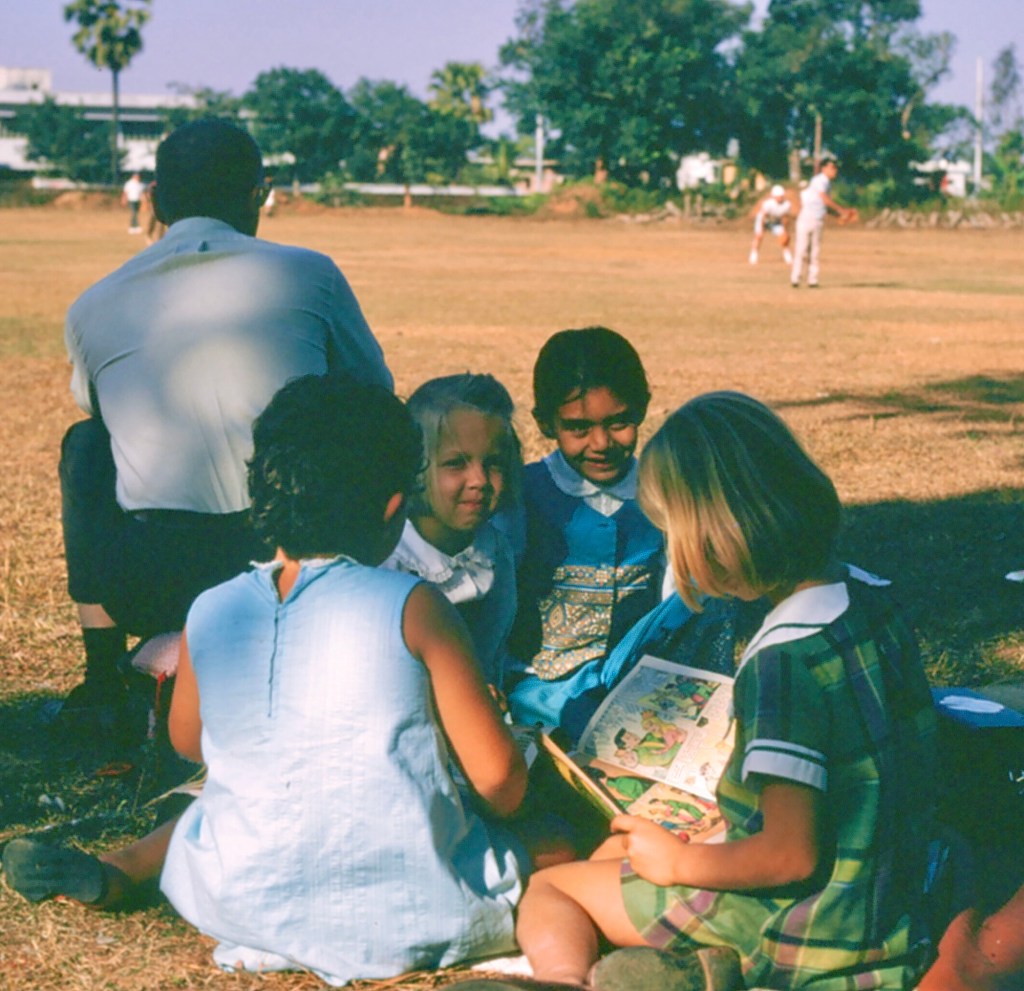
Here’s a familiar story:
This is a story of a layer of social life that doesn’t appear in any contract, law, or job description — and yet, without it, the whole thing quietly falls apart.
Call it the system of imperfect obligations. No single person is required to act. No one is legally on the hook. But someone steps up anyway — and in doing so, they hold something together that would otherwise fracture.
You know these moments when you see them:
The stranger who jumps into a pond to pull out a drowning child. The passing drivers who stop at a roadside crash and stay until help arrives. The employee who becomes a whistleblower, knowing the personal cost, because the fraud had to be exposed. The friend who drives an elderly neighbor to chemotherapy every Tuesday — not because they were asked, but because someone had to.
None of these are rights. They aren’t enforced, and failing to perform them carries no legal penalty. They live in the space between law and love — the domain of norms, trust, and quiet expectation.
What’s remarkable is that this space scales. When a community of people consistently honors these unwritten obligations — not because they must, but because they understand that everyone benefits when they do — something more durable emerges. Consider diamond traders, who conduct enormous transactions on a handshake, backed by centuries of community reputation rather than legal contracts. When trust reaches that kind of density, informal obligation starts to function like institutional infrastructure.
That’s the hidden architecture. Rights protect us from the worst of each other. Laws keep order. But it’s the imperfect obligations — the voluntary, uncompelled acts of people showing up when no one technically has to — that make a community worth living in.
We don’t talk about this enough. Maybe because it can’t be mandated, it gets overlooked in policy. But cultivating it matters: in how we raise children, build organizations, and decide what kind of neighbors we want to be.
The backstop only works if someone is willing to be it.






